D. none of these. causes the kidneys to produce a larger volume of very dilute urine. Alan S.L. It produces concentrated urine by creating an ultrafiltrate from blood. The smooth muscle in the renal pelvis funnels urine via Cortical nephrons (the majority of nephrons) start high in the cortex and have a short loop of Henle which does not penetrate deeply into the medulla. A) The parietal layer of the glomerular capsule is simple squamous epithelium. It produces concentrated urine by creating an ultrafiltrate from blood. It produces concentrated urine by creating an ultrafiltrate from blood. The blood is filtered by two kidneys, which produce urine, a fluid containing toxic substances and waste products. The mammalian nephron is a long tube-like structure, its length varying from 3555 mm long. B. cortical nephrons have an associated vasa recta. C. absorb electrolytes activley with an automatic absorption of water by osmosis. C. absorb electrolytes activley with an automatic absorption of water by osmosis. An incidental consequence of this renal reabsorption of water is A nephron consists of two main parts: a renal corpuscle and its associated renal tubule system. e. vasa recta becomes more concentrated with nitrogenous wastes than the urine. The primary role of the loop of Henle is to enable an organism to produce concentrated urine, not by increasing the tubular concentration, but by rendering the interstitial fluid hypertonic. Emerging from the hilum is the renal pelvis, which is formed from the major and minor calyces in the kidney. The kidneys must produce a minimum urine volume of about 500 mL/day to rid the body of wastes. Similarities Between Cortical Nephron and Juxtamedullary Nephron Most cases of kidney failure display a SpG of about 1.008 to 1.012. Two kidneys, a ureter, a urinary bladder, and a urethra C. Animals such as birds that live in terrestrial environments have more juxtamedullary nephrons than cortical nephrons. The kidneys play a major role in controlling the extracellular fluid volume in the body by producing either a large volume of dilute urine or a small volume of concentrated urine. When the "Execute p1" button is clicked the javascript function p1 is executed. 96)Fetal kidneys do not have to work very hard because? Each kidney consists of an outer renal cortex, an inner renal medulla, and a renal pelvis. From each kidney, the urine flows through a tube, the ureter, to the urinary bladder, where it is stored until it is expelled from the body through another tube, the urethra. Ans: B. a. Australian hopping mice, which live in desert regions, can produce urine concentrated to 9,300 mosm/L25 times as concentrated as their body fluid. reduced in cortical nephrons. The urine is formed in the nephrons and involves the following steps: Glomerular Filtration. Generally, a normal dog's urine SpG will be 1.020 to 1.040. a. Alan S.L. this nice numerical analysis to study differential equation 2. A. What is the correct sequence of organs for the formation and elimination of urine? this nice numerical analysis to study differential equation HP:0030242: Portal vein thrombosis: Thrombosis of the portal vein and/or its tributaries, which include the splenic vein and the superior and inferior mesenteric veins. 263,264 In kidneys, the water and sodium from the glomerular filtrate are reabsorbed in tubules through water channel aquaporins (AQPs) and sodium cortical and juxtamedullary. Nephrons are very minute tiny structures. Vasopressin regulates the tonicity of body fluids. A. cortical nephrons lie almost entirely outside the renal medulla. c) their nephron loop is shorter, with a shorter thin segment. Collecting Duct large amount of water is reabsorbed to produce concentrated urine. Cortical Nephrons: a. Loop of Henles is short and extend only a little into medulla. The process of excretion in humans takes place in the following steps: Urine Formation. The mammalian nephron is a long tube-like structure, its length varying from 3555 mm long. Most cases of kidney failure display a SpG of about 1.008 to 1.012. a: Bladder, urethra, kidney, ureter Eighty-five percent of nephrons are cortical nephrons. Two kidneys, a ureter, a urinary bladder, and a urethra C. The medial-facing hila are tucked into the sweeping convex outline of the cortex. Vasopressin regulates the tonicity of body fluids. An incidental consequence of this renal reabsorption of water is e: The renal corpuscle may be located in the renal cortex or renal medulla. c) their nephron loop is shorter, with a shorter thin segment. Inability of the kidneys to produce either concentrated or dilute urine. Mechanism of concentration of urine The flow of filtrate in two limbs of Henles loop is in opposite direction to form counter current. What is the correct sequence of organs for the formation and elimination of urine? If a water deprivation test is done, where the animal has no access to water for 18 hours, the urine specific gravity goes up (i.e., the urine becomes more concentrated). Ranges of Normal Values in Human Whole Blood (B), Plasma (P), or Serum (S)a Normal Value (Varies with Procedure Used) Determination Traditional Units SI Units Normal Value (Varies with Procedure Used Function. Ranges of Normal Values in Human Whole Blood (B), Plasma (P), or Serum (S)a Normal Value (Varies with Procedure Used) Determination Traditional Units SI Units Normal Value (Varies with Procedure Used Cortical nephrons are different from juxtamedullary nephrons in that a) they do not have a proximal convoluted tubule. Select the correct statement about the nephrons. D. none of these. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards terms like What are the functions of the kidneys?, which is NOT a function of the kidneys in maintaining homeostasis a) regulation of extracellular fluid osmolarity b) regulation of blood hydrogen ion concentration c) regulation of blood glucose concentratoin, THe amount of a substance that is excerted in the urine is equal to the amount Yu MB, BChir, in Brenner and Rector's The Kidney, 2020 Water Homeostasis. The process of excretion in humans takes place in the following steps: Urine Formation. An important enzyme is used to catalyze this mechanism: carbonic anhydrase (CA). A nephron consists of two main parts: a renal corpuscle and its associated renal tubule system. This function: B. cortical nephrons have an associated vasa recta. Mechanism of concentration of urine The flow of filtrate in two limbs of Henles loop is in opposite direction to form counter current. A nephron consists of two main parts: a renal corpuscle and its associated renal tubule system. (50 points)The textarea shown to the left is named ta in a form named f1.It contains the top 10,000 passwords in order of frequency of use -- each followed by a comma (except the last one). 1. A. Urine volume varies considerably. Nephrons located close to the medulla with long nephron loops are called _____ nephrons. Vasopressin, or antidiuretic hormone (AVP), is a nonapeptide synthesized in specialized neurons of the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei.Vasopressin is transported from these nuclei to the posterior pituitary and released in A. fetuses do not have any waste to excrete. Most cases of kidney failure display a SpG of about 1.008 to 1.012. Mechanism of Excretion in Humans. e: The renal corpuscle may be located in the renal cortex or renal medulla. The normal range is one to two liters per day. a: Bladder, urethra, kidney, ureter Eighty-five percent of nephrons are cortical nephrons. A. fetuses do not have any waste to excrete. The ability to form concentrated urine depends on the functions of the A) proximal convoluted tubule. The kidneys are surrounded by three layers of tissue: It is released from the posterior pituitary in response to hypertonicity and causes the kidneys to reabsorb solute-free water and return it to the circulation from the tubules of the nephron, thus returning the tonicity of the body fluids toward normal. Water homeostasis is regulated by a high-gain feedback mechanism that involves the hypothalamus, neurohypophysis, and kidneys. Structure of Nephrons. If: A. glomerular fi ltration rate is low. Mechanism of concentration of urine The flow of filtrate in two limbs of Henles loop is in opposite direction to form counter current. The kidneys are surrounded by three layers of tissue: 2. e: The renal corpuscle may be located in the renal cortex or renal medulla. Cortical nephrons (the majority of nephrons) start high in the cortex and have a short loop of Henle which does not penetrate deeply into the medulla. Australian hopping mice, which live in desert regions, can produce urine concentrated to 9,300 mosm/L25 times as concentrated as their body fluid. Yu MB, BChir, in Brenner and Rector's The Kidney, 2020 Water Homeostasis. Their function is to filter blood and produce urine. 96)Fetal kidneys do not have to work very hard because? An important enzyme is used to catalyze this mechanism: carbonic anhydrase (CA). The kidneys are stimulated to produce renin _____. If: A. glomerular fi ltration rate is low. Under what conditions will the kidney produce concentrated urine? The renal hilum is the entry and exit site for structures servicing the kidneys: vessels, nerves, lymphatics, and ureters. d) they produce urine, whereas juxtamedullary nephrons do not. Each kidney consists of a cortex, medulla and calyces. Output below this level may be caused by severe dehydration or renal disease and is termed oliguria. Blood is filtered in the renal cortex.The renal medulla contains the renal pyramids, where urine formation takes place. Generally, a normal dog's urine SpG will be 1.020 to 1.040. Nephrons are very minute tiny structures. Ranges of Normal Values in Human Whole Blood (B), Plasma (P), or Serum (S)a Normal Value (Varies with Procedure Used) Determination Traditional Units SI Units Normal Value (Varies with Procedure Used Under what conditions will the kidney produce concentrated urine? It is released from the posterior pituitary in response to hypertonicity and causes the kidneys to reabsorb solute-free water and return it to the circulation from the tubules of the nephron, thus returning the tonicity of the body fluids toward normal. HP:0030163: Abnormal vascular physiology: Abnormality of vascular function. If a water deprivation test is done, where the animal has no access to water for 18 hours, the urine specific gravity goes up (i.e., the urine becomes more concentrated). Renal Hilum. HP:0030163: Abnormal vascular physiology: Abnormality of vascular function. Vasopressin (Antidiuretic Hormone) and Water Reabsorption. Animals such as birds that live in terrestrial environments have more juxtamedullary nephrons than cortical nephrons. Function. b) they are much less abundant. Structure of Nephron. Generally, a normal dog's urine SpG will be 1.020 to 1.040. A) The parietal layer of the glomerular capsule is simple squamous epithelium. A) The parietal layer of the glomerular capsule is simple squamous epithelium. The virtual absence of urine production is termed anuria. When the "Execute p1" button is clicked the javascript function p1 is executed. 263,264 In kidneys, the water and sodium from the glomerular filtrate are reabsorbed in tubules through water channel aquaporins (AQPs) and sodium Renal Hilum. Vasopressin (Antidiuretic Hormone) and Water Reabsorption. Each kidney consists of an outer renal cortex, an inner renal medulla, and a renal pelvis. Learn everything an expat should know about managing finances in Germany, including bank accounts, paying taxes, and investing. The Henles loop and vasa recta play a significant role in this. c) their nephron loop is shorter, with a shorter thin segment. The flow of filtrate in A. cortical nephrons lie almost entirely outside the renal medulla. Structure of Nephron. reduced in cortical nephrons. The kidneys play a major role in controlling the extracellular fluid volume in the body by producing either a large volume of dilute urine or a small volume of concentrated urine.

The Henles loop and vasa recta play a significant role in this. Mechanism of Excretion in Humans. Two kidneys, two urethrae, a ureter, and a urinary bladder B. In the human kidney, about 80% of the nephrons, the cortical nephrons, have reduced loops of Henle and are almost entirely confined to the renal cortex. The concentration gradient that exists in the medulla of the kidney is produced by the: A. loops of the cortical nephrons B. proximal convoluted tubules The brain signals the urinary bladder to contract and through the urinary opening called the urethra, we excrete the urine. HP:0030242: Portal vein thrombosis: Thrombosis of the portal vein and/or its tributaries, which include the splenic vein and the superior and inferior mesenteric veins. The ability to form concentrated urine depends on the functions of the A) proximal convoluted tubule. The normal range is one to two liters per day. 96)Fetal kidneys do not have to work very hard because? The medial-facing hila are tucked into the sweeping convex outline of the cortex. There are about millions of nephrons in each human kidney. The virtual absence of urine production is termed anuria. 1. B. form a large volume of very dilute urine or a small volume of very concentrated urine. If: A. glomerular fi ltration rate is low. Yu MB, BChir, in Brenner and Rector's The Kidney, 2020 Water Homeostasis. C. absorb electrolytes activley with an automatic absorption of water by osmosis. a: Bladder, urethra, kidney, ureter Eighty-five percent of nephrons are cortical nephrons. The process of excretion in humans takes place in the following steps: Urine Formation. Australian hopping mice, which live in desert regions, can produce urine concentrated to 9,300 mosm/L25 times as concentrated as their body fluid. This same enzyme and reaction is used in red blood cells in the transportation of CO 2, in the stomach to produce hydrochloric acid, and in the pancreas to produce HCO 3 to buffer acidic chyme from the stomach. Vasopressin regulates the tonicity of body fluids. The medial-facing hila are tucked into the sweeping convex outline of the cortex. B. form a large volume of very dilute urine or a small volume of very concentrated urine. From each kidney, the urine flows through a tube, the ureter, to the urinary bladder, where it is stored until it is expelled from the body through another tube, the urethra. 263,264 In kidneys, the water and sodium from the glomerular filtrate are reabsorbed in tubules through water channel aquaporins (AQPs) and sodium e. vasa recta becomes more concentrated with nitrogenous wastes than the urine. Structure of Nephron. Inability of the kidneys to produce either concentrated or dilute urine. Similarities Between Cortical Nephron and Juxtamedullary Nephron Structure of Nephrons. The kidneys must produce a minimum urine volume of about 500 mL/day to rid the body of wastes. Structure of Nephrons. The Henles loop and vasa recta play a significant role in this. This is also the region where the maximum reabsorption of water takes place to produce concentrated urine. reduced in cortical nephrons. B. glomerular filtration rate is high. The normal range is one to two liters per day. A. cortical nephrons lie almost entirely outside the renal medulla. The action of ADH on the cortical collecting duct allows for the production of concentrated urine and protects against dehydration. If a water deprivation test is done, where the animal has no access to water for 18 hours, the urine specific gravity goes up (i.e., the urine becomes more concentrated). Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards terms like What are the functions of the kidneys?, which is NOT a function of the kidneys in maintaining homeostasis a) regulation of extracellular fluid osmolarity b) regulation of blood hydrogen ion concentration c) regulation of blood glucose concentratoin, THe amount of a substance that is excerted in the urine is equal to the amount The flow of filtrate in HP:0030242: Portal vein thrombosis: Thrombosis of the portal vein and/or its tributaries, which include the splenic vein and the superior and inferior mesenteric veins. The smooth muscle in the renal pelvis funnels urine via Urine passes from the renal pyramids into the renal pelvis.This funnel-shaped structure occupies the central cavity of each kidney and then narrows as it Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards terms like What are the functions of the kidneys?, which is NOT a function of the kidneys in maintaining homeostasis a) regulation of extracellular fluid osmolarity b) regulation of blood hydrogen ion concentration c) regulation of blood glucose concentratoin, THe amount of a substance that is excerted in the urine is equal to the amount 19.2 URINE FORMATION Urine formation involves three main processes namely, glomerular filtration, reabsorption and secretion, that takes place in different parts of Mammals have the ability to produce a concentrated urine. John Feehally DM, FRCP, in Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology, 2019. B. glomerular filtration rate is high. Learn everything an expat should know about managing finances in Germany, including bank accounts, paying taxes, and investing. Output below this level may be caused by severe dehydration or renal disease and is termed oliguria. The kidneys are stimulated to produce renin _____. 19.2 URINE FORMATION Urine formation involves three main processes namely, glomerular filtration, reabsorption and secretion, that takes place in different parts of Mammals have the ability to produce a concentrated urine. The brain signals the urinary bladder to contract and through the urinary opening called the urethra, we excrete the urine. Urine passes from the renal pyramids into the renal pelvis.This funnel-shaped structure occupies the central cavity of each kidney and then narrows as it A. John Feehally DM, FRCP, in Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology, 2019. The blood is filtered by two kidneys, which produce urine, a fluid containing toxic substances and waste products. Vasopressin, or antidiuretic hormone (AVP), is a nonapeptide synthesized in specialized neurons of the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei.Vasopressin is transported from these nuclei to the posterior pituitary and released in

Water homeostasis is regulated by a high-gain feedback mechanism that involves the hypothalamus, neurohypophysis, and kidneys. (50 points)The textarea shown to the left is named ta in a form named f1.It contains the top 10,000 passwords in order of frequency of use -- each followed by a comma (except the last one). Each kidney consists of a cortex, medulla and calyces. A. fetuses do not have any waste to excrete. Under what conditions will the kidney produce concentrated urine? There are about millions of nephrons in each human kidney. Ans: B. What organs compose the Urinary System? causes the kidneys to produce a larger volume of very dilute urine. The absorption of more water by the vasa recta may produce more concentrated urine while the less reabsorption of water may produce diluted urine. Blood is filtered in the renal cortex.The renal medulla contains the renal pyramids, where urine formation takes place. Ans: B. The urine is formed in the nephrons and involves the following steps: Glomerular Filtration. The blood is filtered by two kidneys, which produce urine, a fluid containing toxic substances and waste products. Cortical Nephrons: a. Loop of Henles is short and extend only a little into medulla. Emerging from the hilum is the renal pelvis, which is formed from the major and minor calyces in the kidney.
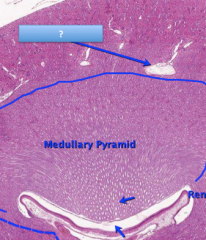
Each kidney consists of an outer renal cortex, an inner renal medulla, and a renal pelvis. The primary role of the loop of Henle is to enable an organism to produce concentrated urine, not by increasing the tubular concentration, but by rendering the interstitial fluid hypertonic. Inability of the kidneys to produce either concentrated or dilute urine. The number of nephrons per kidney can reach to are about 1.000.000 nephrons per kidney. The brain signals the urinary bladder to contract and through the urinary opening called the urethra, we excrete the urine. The action of ADH on the cortical collecting duct allows for the production of concentrated urine and protects against dehydration. This function: Select the correct statement about the nephrons. cortical and juxtamedullary. In the human kidney, about 80% of the nephrons, the cortical nephrons, have reduced loops of Henle and are almost entirely confined to the renal cortex. The distal convoluted tubules from multiple nephrons then drain into a collecting duct, which drains urine deeper into the kidney to be What is the correct sequence of organs for the formation and elimination of urine? causes the kidneys to produce a larger volume of very dilute urine. An important enzyme is used to catalyze this mechanism: carbonic anhydrase (CA). Urine passes from the renal pyramids into the renal pelvis.This funnel-shaped structure occupies the central cavity of each kidney and then narrows as it Nephrons located close to the medulla with long nephron loops are called _____ nephrons. The mammalian nephron is a long tube-like structure, its length varying from 3555 mm long. The virtual absence of urine production is termed anuria. Blood is filtered in the renal cortex.The renal medulla contains the renal pyramids, where urine formation takes place. This same enzyme and reaction is used in red blood cells in the transportation of CO 2, in the stomach to produce hydrochloric acid, and in the pancreas to produce HCO 3 to buffer acidic chyme from the stomach. The concentration gradient that exists in the medulla of the kidney is produced by the: A. loops of the cortical nephrons B. proximal convoluted tubules (50 points)The textarea shown to the left is named ta in a form named f1.It contains the top 10,000 passwords in order of frequency of use -- each followed by a comma (except the last one). What organs compose the Urinary System? HP:0030163: Abnormal vascular physiology: Abnormality of vascular function. Their function is to filter blood and produce urine. a. Animals such as birds that live in terrestrial environments have more juxtamedullary nephrons than cortical nephrons. The renal hilum is the entry and exit site for structures servicing the kidneys: vessels, nerves, lymphatics, and ureters. The kidneys are surrounded by three layers of tissue: this nice numerical analysis to study differential equation Learn everything an expat should know about managing finances in Germany, including bank accounts, paying taxes, and investing. Two kidneys, a ureter, a urinary bladder, and a urethra C. In the human kidney, about 80% of the nephrons, the cortical nephrons, have reduced loops of Henle and are almost entirely confined to the renal cortex. The absorption of more water by the vasa recta may produce more concentrated urine while the less reabsorption of water may produce diluted urine. The action of ADH on the cortical collecting duct allows for the production of concentrated urine and protects against dehydration. Similarities Between Cortical Nephron and Juxtamedullary Nephron The primary role of the loop of Henle is to enable an organism to produce concentrated urine, not by increasing the tubular concentration, but by rendering the interstitial fluid hypertonic. The kidneys are stimulated to produce renin _____. The number of nephrons per kidney can reach to are about 1.000.000 nephrons per kidney.
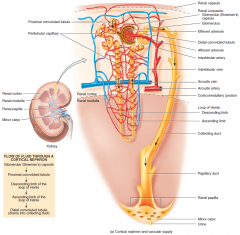
Water homeostasis is regulated by a high-gain feedback mechanism that involves the hypothalamus, neurohypophysis, and kidneys. Browse our listings to find jobs in Germany for expats, including jobs for English speakers or those in your native language. cortical and juxtamedullary. 19.2 URINE FORMATION Urine formation involves three main processes namely, glomerular filtration, reabsorption and secretion, that takes place in different parts of Mammals have the ability to produce a concentrated urine. Cortical Nephrons: a. Loop of Henles is short and extend only a little into medulla. Urine volume varies considerably. This function: Collecting Duct large amount of water is reabsorbed to produce concentrated urine. Cortical nephrons are different from juxtamedullary nephrons in that a) they do not have a proximal convoluted tubule. It is released from the posterior pituitary in response to hypertonicity and causes the kidneys to reabsorb solute-free water and return it to the circulation from the tubules of the nephron, thus returning the tonicity of the body fluids toward normal. Two kidneys, two urethrae, a ureter, and a urinary bladder B. The urine is formed in the nephrons and involves the following steps: Glomerular Filtration. The kidneys play a major role in controlling the extracellular fluid volume in the body by producing either a large volume of dilute urine or a small volume of concentrated urine. The number of nephrons per kidney can reach to are about 1.000.000 nephrons per kidney. Cortical nephrons (the majority of nephrons) start high in the cortex and have a short loop of Henle which does not penetrate deeply into the medulla. John Feehally DM, FRCP, in Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology, 2019. The kidneys must produce a minimum urine volume of about 500 mL/day to rid the body of wastes. B. glomerular filtration rate is high. Each kidney consists of a cortex, medulla and calyces. Nephrons are very minute tiny structures. Vasopressin, or antidiuretic hormone (AVP), is a nonapeptide synthesized in specialized neurons of the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei.Vasopressin is transported from these nuclei to the posterior pituitary and released in Collecting Duct large amount of water is reabsorbed to produce concentrated urine. Select the correct statement about the nephrons. The smooth muscle in the renal pelvis funnels urine via The ability to form concentrated urine depends on the functions of the A) proximal convoluted tubule. Their function is to filter blood and produce urine. The flow of filtrate in b) they are much less abundant. Emerging from the hilum is the renal pelvis, which is formed from the major and minor calyces in the kidney. Output below this level may be caused by severe dehydration or renal disease and is termed oliguria. An incidental consequence of this renal reabsorption of water is The absorption of more water by the vasa recta may produce more concentrated urine while the less reabsorption of water may produce diluted urine. d) they produce urine, whereas juxtamedullary nephrons do not. e. vasa recta becomes more concentrated with nitrogenous wastes than the urine. The renal hilum is the entry and exit site for structures servicing the kidneys: vessels, nerves, lymphatics, and ureters. Mechanism of Excretion in Humans. This is also the region where the maximum reabsorption of water takes place to produce concentrated urine. B. form a large volume of very dilute urine or a small volume of very concentrated urine. B. cortical nephrons have an associated vasa recta. There are about millions of nephrons in each human kidney. This is also the region where the maximum reabsorption of water takes place to produce concentrated urine. Nephrons located close to the medulla with long nephron loops are called _____ nephrons. Browse our listings to find jobs in Germany for expats, including jobs for English speakers or those in your native language. Two kidneys, two urethrae, a ureter, and a urinary bladder B. Cortical nephrons are different from juxtamedullary nephrons in that a) they do not have a proximal convoluted tubule. Urine volume varies considerably. From each kidney, the urine flows through a tube, the ureter, to the urinary bladder, where it is stored until it is expelled from the body through another tube, the urethra. Renal Hilum. Browse our listings to find jobs in Germany for expats, including jobs for English speakers or those in your native language. When the "Execute p1" button is clicked the javascript function p1 is executed. What organs compose the Urinary System? Function. 2. The distal convoluted tubules from multiple nephrons then drain into a collecting duct, which drains urine deeper into the kidney to be Vasopressin (Antidiuretic Hormone) and Water Reabsorption. This same enzyme and reaction is used in red blood cells in the transportation of CO 2, in the stomach to produce hydrochloric acid, and in the pancreas to produce HCO 3 to buffer acidic chyme from the stomach. d) they produce urine, whereas juxtamedullary nephrons do not. b) they are much less abundant. Alan S.L. 1. D. none of these.
 The Henles loop and vasa recta play a significant role in this. Mechanism of Excretion in Humans. Two kidneys, two urethrae, a ureter, and a urinary bladder B. In the human kidney, about 80% of the nephrons, the cortical nephrons, have reduced loops of Henle and are almost entirely confined to the renal cortex. The concentration gradient that exists in the medulla of the kidney is produced by the: A. loops of the cortical nephrons B. proximal convoluted tubules The brain signals the urinary bladder to contract and through the urinary opening called the urethra, we excrete the urine. HP:0030242: Portal vein thrombosis: Thrombosis of the portal vein and/or its tributaries, which include the splenic vein and the superior and inferior mesenteric veins. The ability to form concentrated urine depends on the functions of the A) proximal convoluted tubule. The normal range is one to two liters per day. 96)Fetal kidneys do not have to work very hard because? The medial-facing hila are tucked into the sweeping convex outline of the cortex. There are about millions of nephrons in each human kidney. The virtual absence of urine production is termed anuria. 1. B. form a large volume of very dilute urine or a small volume of very concentrated urine. If: A. glomerular fi ltration rate is low. Yu MB, BChir, in Brenner and Rector's The Kidney, 2020 Water Homeostasis. C. absorb electrolytes activley with an automatic absorption of water by osmosis. a: Bladder, urethra, kidney, ureter Eighty-five percent of nephrons are cortical nephrons. The process of excretion in humans takes place in the following steps: Urine Formation. Australian hopping mice, which live in desert regions, can produce urine concentrated to 9,300 mosm/L25 times as concentrated as their body fluid. This same enzyme and reaction is used in red blood cells in the transportation of CO 2, in the stomach to produce hydrochloric acid, and in the pancreas to produce HCO 3 to buffer acidic chyme from the stomach. Vasopressin regulates the tonicity of body fluids. The medial-facing hila are tucked into the sweeping convex outline of the cortex. B. form a large volume of very dilute urine or a small volume of very concentrated urine. From each kidney, the urine flows through a tube, the ureter, to the urinary bladder, where it is stored until it is expelled from the body through another tube, the urethra. 263,264 In kidneys, the water and sodium from the glomerular filtrate are reabsorbed in tubules through water channel aquaporins (AQPs) and sodium e. vasa recta becomes more concentrated with nitrogenous wastes than the urine. Structure of Nephron. Inability of the kidneys to produce either concentrated or dilute urine. Similarities Between Cortical Nephron and Juxtamedullary Nephron Structure of Nephrons. The kidneys must produce a minimum urine volume of about 500 mL/day to rid the body of wastes. Structure of Nephrons. The Henles loop and vasa recta play a significant role in this. This is also the region where the maximum reabsorption of water takes place to produce concentrated urine. reduced in cortical nephrons. B. glomerular filtration rate is high. The normal range is one to two liters per day. A. cortical nephrons lie almost entirely outside the renal medulla. The action of ADH on the cortical collecting duct allows for the production of concentrated urine and protects against dehydration. If a water deprivation test is done, where the animal has no access to water for 18 hours, the urine specific gravity goes up (i.e., the urine becomes more concentrated). Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards terms like What are the functions of the kidneys?, which is NOT a function of the kidneys in maintaining homeostasis a) regulation of extracellular fluid osmolarity b) regulation of blood hydrogen ion concentration c) regulation of blood glucose concentratoin, THe amount of a substance that is excerted in the urine is equal to the amount The flow of filtrate in HP:0030242: Portal vein thrombosis: Thrombosis of the portal vein and/or its tributaries, which include the splenic vein and the superior and inferior mesenteric veins. The smooth muscle in the renal pelvis funnels urine via Urine passes from the renal pyramids into the renal pelvis.This funnel-shaped structure occupies the central cavity of each kidney and then narrows as it Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards terms like What are the functions of the kidneys?, which is NOT a function of the kidneys in maintaining homeostasis a) regulation of extracellular fluid osmolarity b) regulation of blood hydrogen ion concentration c) regulation of blood glucose concentratoin, THe amount of a substance that is excerted in the urine is equal to the amount 19.2 URINE FORMATION Urine formation involves three main processes namely, glomerular filtration, reabsorption and secretion, that takes place in different parts of Mammals have the ability to produce a concentrated urine. John Feehally DM, FRCP, in Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology, 2019. B. glomerular filtration rate is high. Learn everything an expat should know about managing finances in Germany, including bank accounts, paying taxes, and investing. Output below this level may be caused by severe dehydration or renal disease and is termed oliguria. The kidneys are stimulated to produce renin _____. 19.2 URINE FORMATION Urine formation involves three main processes namely, glomerular filtration, reabsorption and secretion, that takes place in different parts of Mammals have the ability to produce a concentrated urine. The brain signals the urinary bladder to contract and through the urinary opening called the urethra, we excrete the urine. Urine passes from the renal pyramids into the renal pelvis.This funnel-shaped structure occupies the central cavity of each kidney and then narrows as it A. John Feehally DM, FRCP, in Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology, 2019. The blood is filtered by two kidneys, which produce urine, a fluid containing toxic substances and waste products. Vasopressin, or antidiuretic hormone (AVP), is a nonapeptide synthesized in specialized neurons of the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei.Vasopressin is transported from these nuclei to the posterior pituitary and released in
The Henles loop and vasa recta play a significant role in this. Mechanism of Excretion in Humans. Two kidneys, two urethrae, a ureter, and a urinary bladder B. In the human kidney, about 80% of the nephrons, the cortical nephrons, have reduced loops of Henle and are almost entirely confined to the renal cortex. The concentration gradient that exists in the medulla of the kidney is produced by the: A. loops of the cortical nephrons B. proximal convoluted tubules The brain signals the urinary bladder to contract and through the urinary opening called the urethra, we excrete the urine. HP:0030242: Portal vein thrombosis: Thrombosis of the portal vein and/or its tributaries, which include the splenic vein and the superior and inferior mesenteric veins. The ability to form concentrated urine depends on the functions of the A) proximal convoluted tubule. The normal range is one to two liters per day. 96)Fetal kidneys do not have to work very hard because? The medial-facing hila are tucked into the sweeping convex outline of the cortex. There are about millions of nephrons in each human kidney. The virtual absence of urine production is termed anuria. 1. B. form a large volume of very dilute urine or a small volume of very concentrated urine. If: A. glomerular fi ltration rate is low. Yu MB, BChir, in Brenner and Rector's The Kidney, 2020 Water Homeostasis. C. absorb electrolytes activley with an automatic absorption of water by osmosis. a: Bladder, urethra, kidney, ureter Eighty-five percent of nephrons are cortical nephrons. The process of excretion in humans takes place in the following steps: Urine Formation. Australian hopping mice, which live in desert regions, can produce urine concentrated to 9,300 mosm/L25 times as concentrated as their body fluid. This same enzyme and reaction is used in red blood cells in the transportation of CO 2, in the stomach to produce hydrochloric acid, and in the pancreas to produce HCO 3 to buffer acidic chyme from the stomach. Vasopressin regulates the tonicity of body fluids. The medial-facing hila are tucked into the sweeping convex outline of the cortex. B. form a large volume of very dilute urine or a small volume of very concentrated urine. From each kidney, the urine flows through a tube, the ureter, to the urinary bladder, where it is stored until it is expelled from the body through another tube, the urethra. 263,264 In kidneys, the water and sodium from the glomerular filtrate are reabsorbed in tubules through water channel aquaporins (AQPs) and sodium e. vasa recta becomes more concentrated with nitrogenous wastes than the urine. Structure of Nephron. Inability of the kidneys to produce either concentrated or dilute urine. Similarities Between Cortical Nephron and Juxtamedullary Nephron Structure of Nephrons. The kidneys must produce a minimum urine volume of about 500 mL/day to rid the body of wastes. Structure of Nephrons. The Henles loop and vasa recta play a significant role in this. This is also the region where the maximum reabsorption of water takes place to produce concentrated urine. reduced in cortical nephrons. B. glomerular filtration rate is high. The normal range is one to two liters per day. A. cortical nephrons lie almost entirely outside the renal medulla. The action of ADH on the cortical collecting duct allows for the production of concentrated urine and protects against dehydration. If a water deprivation test is done, where the animal has no access to water for 18 hours, the urine specific gravity goes up (i.e., the urine becomes more concentrated). Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards terms like What are the functions of the kidneys?, which is NOT a function of the kidneys in maintaining homeostasis a) regulation of extracellular fluid osmolarity b) regulation of blood hydrogen ion concentration c) regulation of blood glucose concentratoin, THe amount of a substance that is excerted in the urine is equal to the amount The flow of filtrate in HP:0030242: Portal vein thrombosis: Thrombosis of the portal vein and/or its tributaries, which include the splenic vein and the superior and inferior mesenteric veins. The smooth muscle in the renal pelvis funnels urine via Urine passes from the renal pyramids into the renal pelvis.This funnel-shaped structure occupies the central cavity of each kidney and then narrows as it Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards terms like What are the functions of the kidneys?, which is NOT a function of the kidneys in maintaining homeostasis a) regulation of extracellular fluid osmolarity b) regulation of blood hydrogen ion concentration c) regulation of blood glucose concentratoin, THe amount of a substance that is excerted in the urine is equal to the amount 19.2 URINE FORMATION Urine formation involves three main processes namely, glomerular filtration, reabsorption and secretion, that takes place in different parts of Mammals have the ability to produce a concentrated urine. John Feehally DM, FRCP, in Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology, 2019. B. glomerular filtration rate is high. Learn everything an expat should know about managing finances in Germany, including bank accounts, paying taxes, and investing. Output below this level may be caused by severe dehydration or renal disease and is termed oliguria. The kidneys are stimulated to produce renin _____. 19.2 URINE FORMATION Urine formation involves three main processes namely, glomerular filtration, reabsorption and secretion, that takes place in different parts of Mammals have the ability to produce a concentrated urine. The brain signals the urinary bladder to contract and through the urinary opening called the urethra, we excrete the urine. Urine passes from the renal pyramids into the renal pelvis.This funnel-shaped structure occupies the central cavity of each kidney and then narrows as it A. John Feehally DM, FRCP, in Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology, 2019. The blood is filtered by two kidneys, which produce urine, a fluid containing toxic substances and waste products. Vasopressin, or antidiuretic hormone (AVP), is a nonapeptide synthesized in specialized neurons of the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei.Vasopressin is transported from these nuclei to the posterior pituitary and released in  Water homeostasis is regulated by a high-gain feedback mechanism that involves the hypothalamus, neurohypophysis, and kidneys. (50 points)The textarea shown to the left is named ta in a form named f1.It contains the top 10,000 passwords in order of frequency of use -- each followed by a comma (except the last one). Each kidney consists of a cortex, medulla and calyces. A. fetuses do not have any waste to excrete. Under what conditions will the kidney produce concentrated urine? There are about millions of nephrons in each human kidney. Ans: B. What organs compose the Urinary System? causes the kidneys to produce a larger volume of very dilute urine. The absorption of more water by the vasa recta may produce more concentrated urine while the less reabsorption of water may produce diluted urine. Blood is filtered in the renal cortex.The renal medulla contains the renal pyramids, where urine formation takes place. Ans: B. The urine is formed in the nephrons and involves the following steps: Glomerular Filtration. The blood is filtered by two kidneys, which produce urine, a fluid containing toxic substances and waste products. Cortical Nephrons: a. Loop of Henles is short and extend only a little into medulla. Emerging from the hilum is the renal pelvis, which is formed from the major and minor calyces in the kidney.
Water homeostasis is regulated by a high-gain feedback mechanism that involves the hypothalamus, neurohypophysis, and kidneys. (50 points)The textarea shown to the left is named ta in a form named f1.It contains the top 10,000 passwords in order of frequency of use -- each followed by a comma (except the last one). Each kidney consists of a cortex, medulla and calyces. A. fetuses do not have any waste to excrete. Under what conditions will the kidney produce concentrated urine? There are about millions of nephrons in each human kidney. Ans: B. What organs compose the Urinary System? causes the kidneys to produce a larger volume of very dilute urine. The absorption of more water by the vasa recta may produce more concentrated urine while the less reabsorption of water may produce diluted urine. Blood is filtered in the renal cortex.The renal medulla contains the renal pyramids, where urine formation takes place. Ans: B. The urine is formed in the nephrons and involves the following steps: Glomerular Filtration. The blood is filtered by two kidneys, which produce urine, a fluid containing toxic substances and waste products. Cortical Nephrons: a. Loop of Henles is short and extend only a little into medulla. Emerging from the hilum is the renal pelvis, which is formed from the major and minor calyces in the kidney.  Each kidney consists of an outer renal cortex, an inner renal medulla, and a renal pelvis. The primary role of the loop of Henle is to enable an organism to produce concentrated urine, not by increasing the tubular concentration, but by rendering the interstitial fluid hypertonic. Inability of the kidneys to produce either concentrated or dilute urine. The number of nephrons per kidney can reach to are about 1.000.000 nephrons per kidney. The brain signals the urinary bladder to contract and through the urinary opening called the urethra, we excrete the urine. The action of ADH on the cortical collecting duct allows for the production of concentrated urine and protects against dehydration. This function: Select the correct statement about the nephrons. cortical and juxtamedullary. In the human kidney, about 80% of the nephrons, the cortical nephrons, have reduced loops of Henle and are almost entirely confined to the renal cortex. The distal convoluted tubules from multiple nephrons then drain into a collecting duct, which drains urine deeper into the kidney to be What is the correct sequence of organs for the formation and elimination of urine? causes the kidneys to produce a larger volume of very dilute urine. An important enzyme is used to catalyze this mechanism: carbonic anhydrase (CA). Urine passes from the renal pyramids into the renal pelvis.This funnel-shaped structure occupies the central cavity of each kidney and then narrows as it Nephrons located close to the medulla with long nephron loops are called _____ nephrons. The mammalian nephron is a long tube-like structure, its length varying from 3555 mm long. The virtual absence of urine production is termed anuria. Blood is filtered in the renal cortex.The renal medulla contains the renal pyramids, where urine formation takes place. This same enzyme and reaction is used in red blood cells in the transportation of CO 2, in the stomach to produce hydrochloric acid, and in the pancreas to produce HCO 3 to buffer acidic chyme from the stomach. The concentration gradient that exists in the medulla of the kidney is produced by the: A. loops of the cortical nephrons B. proximal convoluted tubules (50 points)The textarea shown to the left is named ta in a form named f1.It contains the top 10,000 passwords in order of frequency of use -- each followed by a comma (except the last one). What organs compose the Urinary System? HP:0030163: Abnormal vascular physiology: Abnormality of vascular function. Their function is to filter blood and produce urine. a. Animals such as birds that live in terrestrial environments have more juxtamedullary nephrons than cortical nephrons. The renal hilum is the entry and exit site for structures servicing the kidneys: vessels, nerves, lymphatics, and ureters. The kidneys are surrounded by three layers of tissue: this nice numerical analysis to study differential equation Learn everything an expat should know about managing finances in Germany, including bank accounts, paying taxes, and investing. Two kidneys, a ureter, a urinary bladder, and a urethra C. In the human kidney, about 80% of the nephrons, the cortical nephrons, have reduced loops of Henle and are almost entirely confined to the renal cortex. The absorption of more water by the vasa recta may produce more concentrated urine while the less reabsorption of water may produce diluted urine. The action of ADH on the cortical collecting duct allows for the production of concentrated urine and protects against dehydration. Similarities Between Cortical Nephron and Juxtamedullary Nephron The primary role of the loop of Henle is to enable an organism to produce concentrated urine, not by increasing the tubular concentration, but by rendering the interstitial fluid hypertonic. The kidneys are stimulated to produce renin _____. The number of nephrons per kidney can reach to are about 1.000.000 nephrons per kidney.
Each kidney consists of an outer renal cortex, an inner renal medulla, and a renal pelvis. The primary role of the loop of Henle is to enable an organism to produce concentrated urine, not by increasing the tubular concentration, but by rendering the interstitial fluid hypertonic. Inability of the kidneys to produce either concentrated or dilute urine. The number of nephrons per kidney can reach to are about 1.000.000 nephrons per kidney. The brain signals the urinary bladder to contract and through the urinary opening called the urethra, we excrete the urine. The action of ADH on the cortical collecting duct allows for the production of concentrated urine and protects against dehydration. This function: Select the correct statement about the nephrons. cortical and juxtamedullary. In the human kidney, about 80% of the nephrons, the cortical nephrons, have reduced loops of Henle and are almost entirely confined to the renal cortex. The distal convoluted tubules from multiple nephrons then drain into a collecting duct, which drains urine deeper into the kidney to be What is the correct sequence of organs for the formation and elimination of urine? causes the kidneys to produce a larger volume of very dilute urine. An important enzyme is used to catalyze this mechanism: carbonic anhydrase (CA). Urine passes from the renal pyramids into the renal pelvis.This funnel-shaped structure occupies the central cavity of each kidney and then narrows as it Nephrons located close to the medulla with long nephron loops are called _____ nephrons. The mammalian nephron is a long tube-like structure, its length varying from 3555 mm long. The virtual absence of urine production is termed anuria. Blood is filtered in the renal cortex.The renal medulla contains the renal pyramids, where urine formation takes place. This same enzyme and reaction is used in red blood cells in the transportation of CO 2, in the stomach to produce hydrochloric acid, and in the pancreas to produce HCO 3 to buffer acidic chyme from the stomach. The concentration gradient that exists in the medulla of the kidney is produced by the: A. loops of the cortical nephrons B. proximal convoluted tubules (50 points)The textarea shown to the left is named ta in a form named f1.It contains the top 10,000 passwords in order of frequency of use -- each followed by a comma (except the last one). What organs compose the Urinary System? HP:0030163: Abnormal vascular physiology: Abnormality of vascular function. Their function is to filter blood and produce urine. a. Animals such as birds that live in terrestrial environments have more juxtamedullary nephrons than cortical nephrons. The renal hilum is the entry and exit site for structures servicing the kidneys: vessels, nerves, lymphatics, and ureters. The kidneys are surrounded by three layers of tissue: this nice numerical analysis to study differential equation Learn everything an expat should know about managing finances in Germany, including bank accounts, paying taxes, and investing. Two kidneys, a ureter, a urinary bladder, and a urethra C. In the human kidney, about 80% of the nephrons, the cortical nephrons, have reduced loops of Henle and are almost entirely confined to the renal cortex. The absorption of more water by the vasa recta may produce more concentrated urine while the less reabsorption of water may produce diluted urine. The action of ADH on the cortical collecting duct allows for the production of concentrated urine and protects against dehydration. Similarities Between Cortical Nephron and Juxtamedullary Nephron The primary role of the loop of Henle is to enable an organism to produce concentrated urine, not by increasing the tubular concentration, but by rendering the interstitial fluid hypertonic. The kidneys are stimulated to produce renin _____. The number of nephrons per kidney can reach to are about 1.000.000 nephrons per kidney.  Water homeostasis is regulated by a high-gain feedback mechanism that involves the hypothalamus, neurohypophysis, and kidneys. Browse our listings to find jobs in Germany for expats, including jobs for English speakers or those in your native language. cortical and juxtamedullary. 19.2 URINE FORMATION Urine formation involves three main processes namely, glomerular filtration, reabsorption and secretion, that takes place in different parts of Mammals have the ability to produce a concentrated urine. Cortical Nephrons: a. Loop of Henles is short and extend only a little into medulla. Urine volume varies considerably. This function: Collecting Duct large amount of water is reabsorbed to produce concentrated urine. Cortical nephrons are different from juxtamedullary nephrons in that a) they do not have a proximal convoluted tubule. It is released from the posterior pituitary in response to hypertonicity and causes the kidneys to reabsorb solute-free water and return it to the circulation from the tubules of the nephron, thus returning the tonicity of the body fluids toward normal. Two kidneys, two urethrae, a ureter, and a urinary bladder B. The urine is formed in the nephrons and involves the following steps: Glomerular Filtration. The kidneys play a major role in controlling the extracellular fluid volume in the body by producing either a large volume of dilute urine or a small volume of concentrated urine. The number of nephrons per kidney can reach to are about 1.000.000 nephrons per kidney. Cortical nephrons (the majority of nephrons) start high in the cortex and have a short loop of Henle which does not penetrate deeply into the medulla. John Feehally DM, FRCP, in Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology, 2019. The kidneys must produce a minimum urine volume of about 500 mL/day to rid the body of wastes. B. glomerular filtration rate is high. Each kidney consists of a cortex, medulla and calyces. Nephrons are very minute tiny structures. Vasopressin, or antidiuretic hormone (AVP), is a nonapeptide synthesized in specialized neurons of the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei.Vasopressin is transported from these nuclei to the posterior pituitary and released in Collecting Duct large amount of water is reabsorbed to produce concentrated urine. Select the correct statement about the nephrons. The smooth muscle in the renal pelvis funnels urine via The ability to form concentrated urine depends on the functions of the A) proximal convoluted tubule. Their function is to filter blood and produce urine. The flow of filtrate in b) they are much less abundant. Emerging from the hilum is the renal pelvis, which is formed from the major and minor calyces in the kidney. Output below this level may be caused by severe dehydration or renal disease and is termed oliguria. An incidental consequence of this renal reabsorption of water is The absorption of more water by the vasa recta may produce more concentrated urine while the less reabsorption of water may produce diluted urine. d) they produce urine, whereas juxtamedullary nephrons do not. e. vasa recta becomes more concentrated with nitrogenous wastes than the urine. The renal hilum is the entry and exit site for structures servicing the kidneys: vessels, nerves, lymphatics, and ureters. Mechanism of Excretion in Humans. This is also the region where the maximum reabsorption of water takes place to produce concentrated urine. B. form a large volume of very dilute urine or a small volume of very concentrated urine. B. cortical nephrons have an associated vasa recta. There are about millions of nephrons in each human kidney. This is also the region where the maximum reabsorption of water takes place to produce concentrated urine. Nephrons located close to the medulla with long nephron loops are called _____ nephrons. Browse our listings to find jobs in Germany for expats, including jobs for English speakers or those in your native language. Two kidneys, two urethrae, a ureter, and a urinary bladder B. Cortical nephrons are different from juxtamedullary nephrons in that a) they do not have a proximal convoluted tubule. Urine volume varies considerably. From each kidney, the urine flows through a tube, the ureter, to the urinary bladder, where it is stored until it is expelled from the body through another tube, the urethra. Renal Hilum. Browse our listings to find jobs in Germany for expats, including jobs for English speakers or those in your native language. When the "Execute p1" button is clicked the javascript function p1 is executed. What organs compose the Urinary System? Function. 2. The distal convoluted tubules from multiple nephrons then drain into a collecting duct, which drains urine deeper into the kidney to be Vasopressin (Antidiuretic Hormone) and Water Reabsorption. This same enzyme and reaction is used in red blood cells in the transportation of CO 2, in the stomach to produce hydrochloric acid, and in the pancreas to produce HCO 3 to buffer acidic chyme from the stomach. d) they produce urine, whereas juxtamedullary nephrons do not. b) they are much less abundant. Alan S.L. 1. D. none of these.
Water homeostasis is regulated by a high-gain feedback mechanism that involves the hypothalamus, neurohypophysis, and kidneys. Browse our listings to find jobs in Germany for expats, including jobs for English speakers or those in your native language. cortical and juxtamedullary. 19.2 URINE FORMATION Urine formation involves three main processes namely, glomerular filtration, reabsorption and secretion, that takes place in different parts of Mammals have the ability to produce a concentrated urine. Cortical Nephrons: a. Loop of Henles is short and extend only a little into medulla. Urine volume varies considerably. This function: Collecting Duct large amount of water is reabsorbed to produce concentrated urine. Cortical nephrons are different from juxtamedullary nephrons in that a) they do not have a proximal convoluted tubule. It is released from the posterior pituitary in response to hypertonicity and causes the kidneys to reabsorb solute-free water and return it to the circulation from the tubules of the nephron, thus returning the tonicity of the body fluids toward normal. Two kidneys, two urethrae, a ureter, and a urinary bladder B. The urine is formed in the nephrons and involves the following steps: Glomerular Filtration. The kidneys play a major role in controlling the extracellular fluid volume in the body by producing either a large volume of dilute urine or a small volume of concentrated urine. The number of nephrons per kidney can reach to are about 1.000.000 nephrons per kidney. Cortical nephrons (the majority of nephrons) start high in the cortex and have a short loop of Henle which does not penetrate deeply into the medulla. John Feehally DM, FRCP, in Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology, 2019. The kidneys must produce a minimum urine volume of about 500 mL/day to rid the body of wastes. B. glomerular filtration rate is high. Each kidney consists of a cortex, medulla and calyces. Nephrons are very minute tiny structures. Vasopressin, or antidiuretic hormone (AVP), is a nonapeptide synthesized in specialized neurons of the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei.Vasopressin is transported from these nuclei to the posterior pituitary and released in Collecting Duct large amount of water is reabsorbed to produce concentrated urine. Select the correct statement about the nephrons. The smooth muscle in the renal pelvis funnels urine via The ability to form concentrated urine depends on the functions of the A) proximal convoluted tubule. Their function is to filter blood and produce urine. The flow of filtrate in b) they are much less abundant. Emerging from the hilum is the renal pelvis, which is formed from the major and minor calyces in the kidney. Output below this level may be caused by severe dehydration or renal disease and is termed oliguria. An incidental consequence of this renal reabsorption of water is The absorption of more water by the vasa recta may produce more concentrated urine while the less reabsorption of water may produce diluted urine. d) they produce urine, whereas juxtamedullary nephrons do not. e. vasa recta becomes more concentrated with nitrogenous wastes than the urine. The renal hilum is the entry and exit site for structures servicing the kidneys: vessels, nerves, lymphatics, and ureters. Mechanism of Excretion in Humans. This is also the region where the maximum reabsorption of water takes place to produce concentrated urine. B. form a large volume of very dilute urine or a small volume of very concentrated urine. B. cortical nephrons have an associated vasa recta. There are about millions of nephrons in each human kidney. This is also the region where the maximum reabsorption of water takes place to produce concentrated urine. Nephrons located close to the medulla with long nephron loops are called _____ nephrons. Browse our listings to find jobs in Germany for expats, including jobs for English speakers or those in your native language. Two kidneys, two urethrae, a ureter, and a urinary bladder B. Cortical nephrons are different from juxtamedullary nephrons in that a) they do not have a proximal convoluted tubule. Urine volume varies considerably. From each kidney, the urine flows through a tube, the ureter, to the urinary bladder, where it is stored until it is expelled from the body through another tube, the urethra. Renal Hilum. Browse our listings to find jobs in Germany for expats, including jobs for English speakers or those in your native language. When the "Execute p1" button is clicked the javascript function p1 is executed. What organs compose the Urinary System? Function. 2. The distal convoluted tubules from multiple nephrons then drain into a collecting duct, which drains urine deeper into the kidney to be Vasopressin (Antidiuretic Hormone) and Water Reabsorption. This same enzyme and reaction is used in red blood cells in the transportation of CO 2, in the stomach to produce hydrochloric acid, and in the pancreas to produce HCO 3 to buffer acidic chyme from the stomach. d) they produce urine, whereas juxtamedullary nephrons do not. b) they are much less abundant. Alan S.L. 1. D. none of these.